What is an FDM 3D Printer?
An FDM (Fused Deposition Model) 3D printer is a tool that creates rapid prototypes through filaments. 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, which is the complete opposite of a subtractive process. While subtractive manufacturing processes like laser cutting and metal bending take away from metal to create parts, additive manufacturing builds parts from a 2D model.
According to Stratasys.com, S. Scott Crump, the founder of Stratasys, used a hot glue gun to melt plastic and poured it into thin layers to make a toy for his daughter. He called the invention of FDM. In 1991, Crump trademarked the term “FDM”. This trademark prevented anyone from using the term until it ended in 2009. This caused others to create FFF 3D Printers to avoid legal trouble.
With an industrial FDM 3D printing machine, the entire print chamber warms up during the printing. In contrast, FFF-based machines are designed without a print chamber. In such devices, the material experiences temperature fluctuations when it’s exposed to a cold environment during its extrusion onto a heated bed.
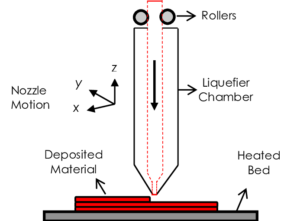
Originally known as rapid prototyping, 3D printing is the process of building 3D solid objects from a digital file. G-code is the most common file format. This file contains coordinates to guide the printer’s movements to print the material. These coordinates guide the printer’s movements, both horizontally and vertically, through the x, y, and z axes.
That is just the beginning process of creating a 3 dimensional object through FDM. There is so much more to the rapid prototyping process.
How the FDM 3D Printer Works
The FDM 3D printer acts much like a normal printer. The printer uses the coordinates to print exactly what it is supposed to. The difference is that unlike normal printers, the 3D printer starts at the bottom and slowly builds up to create the object. Since it uses FDM to build layers, it takes a period of hours to turn 2D prints of a 3D CAD drawing into a three dimensional object. The 3D printer must print over the same area in order to create all the necessary details for layering.
Instead of using ink like a normal printer, FDM 3D printers use a nozzle to extrude molten plastic onto the 3D printer’s platform. The computer with the coordinates coming from the software controls the nozzle. The quality of plastic is very important as well. 3D printers use thermoplastic to build the objects.
Thermoplastic becomes liquid when hot and solid when cold. According to ThoughtCo.com, the polymer has the ability to remold and reheat several times. Thermoplastics also have a boiling point between 6500 and 7250 degrees Fahrenheit. This allows 3D printers to easily build and mold objects so easily.
Once the object completely prints, it must go through a post-processing. The process can vary depending on the project. FDM printers require support structures to facilitate 3D printing’s more complex geometries and their removal represents the last step in post-processing. Depending on the extruder type, the object will either have soluble or insoluble support.
FDM 3D Printer Support Removal
Insoluble Support
The main material of the 3D object is also in the insoluble supports. FDM 3D printers with a single extruder are the only ones that can use this support. The 3D printer prints the supports from the same filament. Depending on the position of the supports, removing these can be difficult.
Soluble Support
HIPS and PVA most commonly make up soluble supports. ABS uses HIPS, while PLA works with PVA. HIPS dissolves in D-limonene, while PVA dissolves in water. Machinists can easily remove soluble supports by simply soaking the object in water or other liquids. This makes the post-processing very easy.
FDM 3D Printer Thermoplastics
FDM printers use multiple types of plastics. Yes, you read that correctly. According to British Plastic Federation, there are many different types of thermoplastics. 3D printers use these thermoplastics the most:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- PLA (polylactic acid)
- PETG (polyethylene gerephthalate glycol)
ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is an opaque thermoplastic and amorphous polymer. ABS melts and becomes liquid at 221 degrees Fahrenheit. Once they heat up, they can cool down and reheat again. Since they don’t burn, they are great for molding and 3D printing. ABS is known world-wide for being the thermoplastic that creates Legos.
ABS most commonly polymerizes through the process of emulsion. According to Britannica, Emulsion is the mixture of liquids that have no mutual solubility. A perfect example of this is mixing oil and water together. The mixture uses a third agent to mix the substances together. The agent for ABS is the heat that turns into liquid.
The only issue is that it isn’t entirely eco-friendly. Refined crude oil makes this plastic. This can be very hazardous to the environment if thrown away.
PLA
Polylactic acid (PLA) is the most popular 3D printing material. Natural materials like corn starch make up the bioplastic and thermoplastic PLA filament. PLA is easy to work with, usually requiring minimal effort to produce quality parts, especially on a 3D printer. Natural or recycled materials create PLA, which makes it eco-friendly and biodegradable. The material also requires lower temperatures, can be printed very quickly in 60 millimeters per second, and is inexpensive. PLA’s extrusion temperature is between 374-428 degrees Fahrenheit.
The only problems with Polylactic acid are that it is brittle, weak, has low temperature and chemical resistance. It is wise to not use this material for outdoor products. Otherwise, it might melt from the heat of the sun. This is a great option for those that want to be eco-friendly.
PETG
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is easily the top quality thermoplastic to use for 3D printing. This material is strong and cost-effective compared to other material like acrylic and polycarbonate. Durable, non-toxic, and fully recyclable, food containers use this material. PETG’s durability rivals even polycarbonate. Polycarbonate is known to be 250 times stronger than glass, making it close to being indestructible.
PETG is a glycol modified version of Polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This material is excellent in colder temperatures. The extrusion point for PETG is higher than PLA’s, between 428 and 500 degrees Fahrenheit. The only downfalls with Polyethylene terephthalate glycol is that it is hard to post process, the price is more expensive than PLA, and it has a softer surface.
6 FDM 3D Printer’s Benefits
To review, FDM 3D printers have these benefits:
- Simple
- Fast
- Efficient
- Reusable filaments
- Cost Effective
- User Friendly
FDM 3D printers were made to be simple and easy to use. Click here to request a quote for your next 3D printing job.
We Are Your Online CNC Machine Shop
Parts Badger creates your exact designed product. We use Instant quoting and 24/7 manufacturing to get your products created and back to you very quickly. Additional machining services include but are not limited to:
Our knowledgeable team of experts will work closely with you to create high-quality components fabricated to your unique specifications, regardless of complexity.


Recent Comments